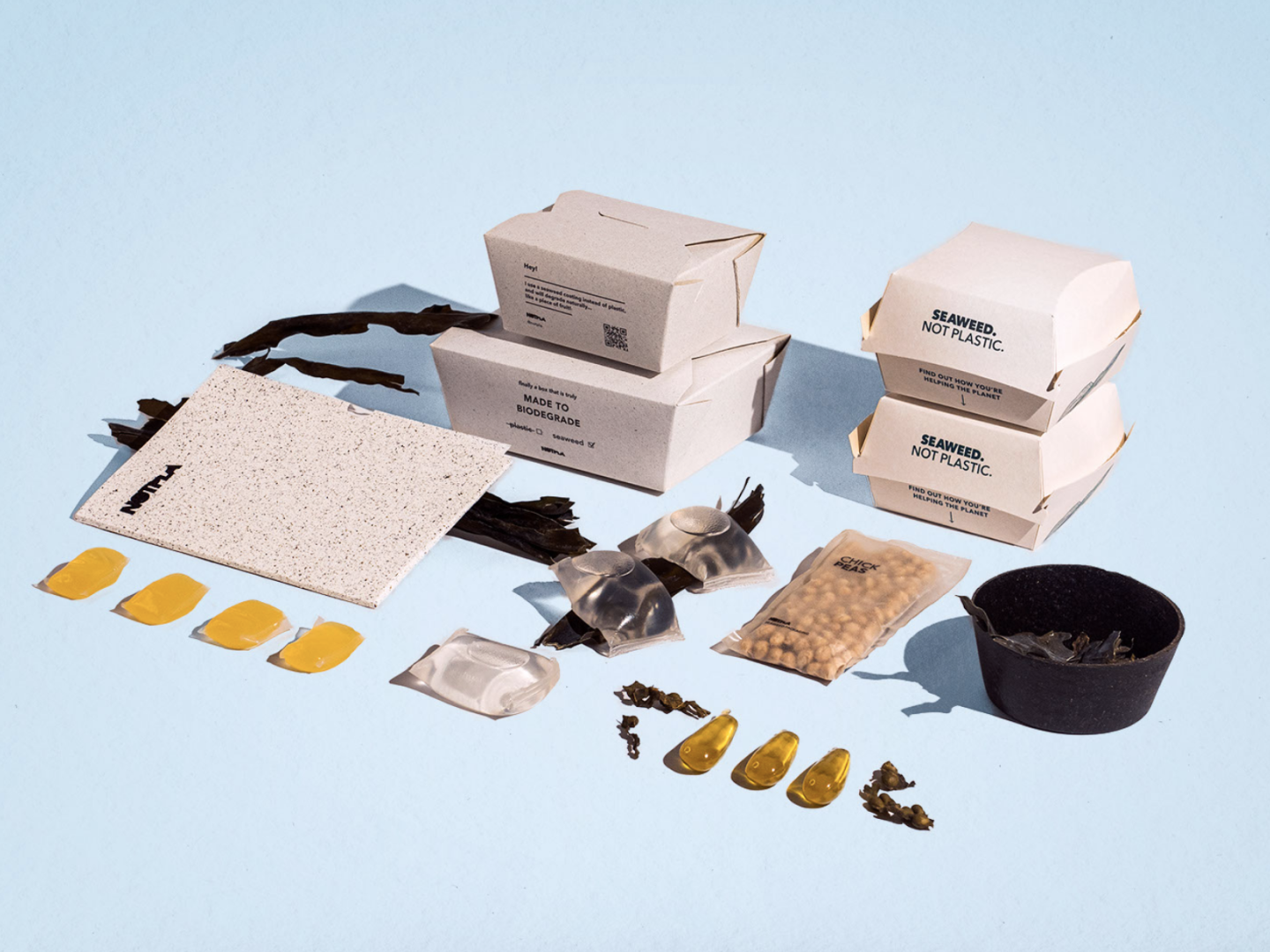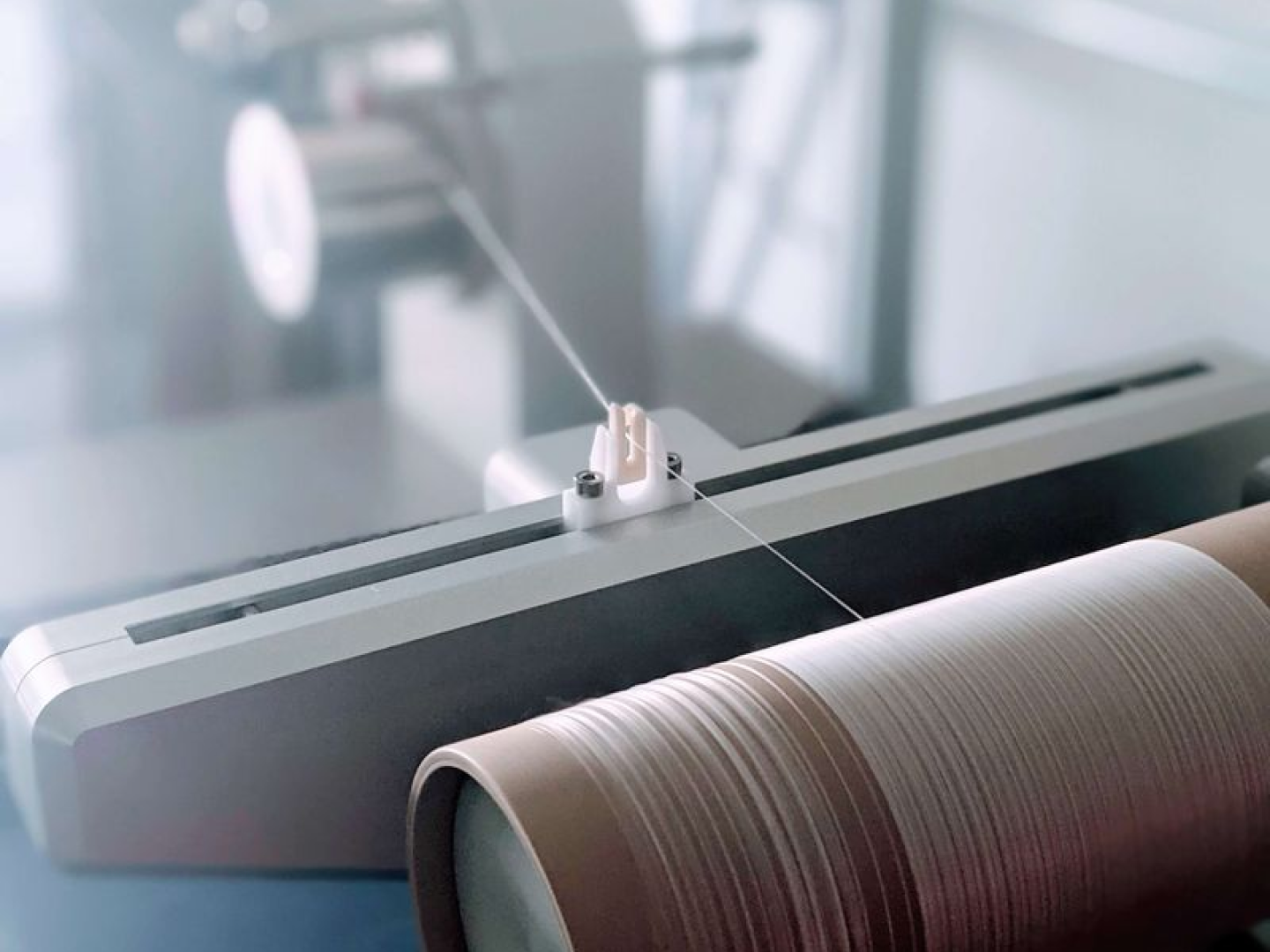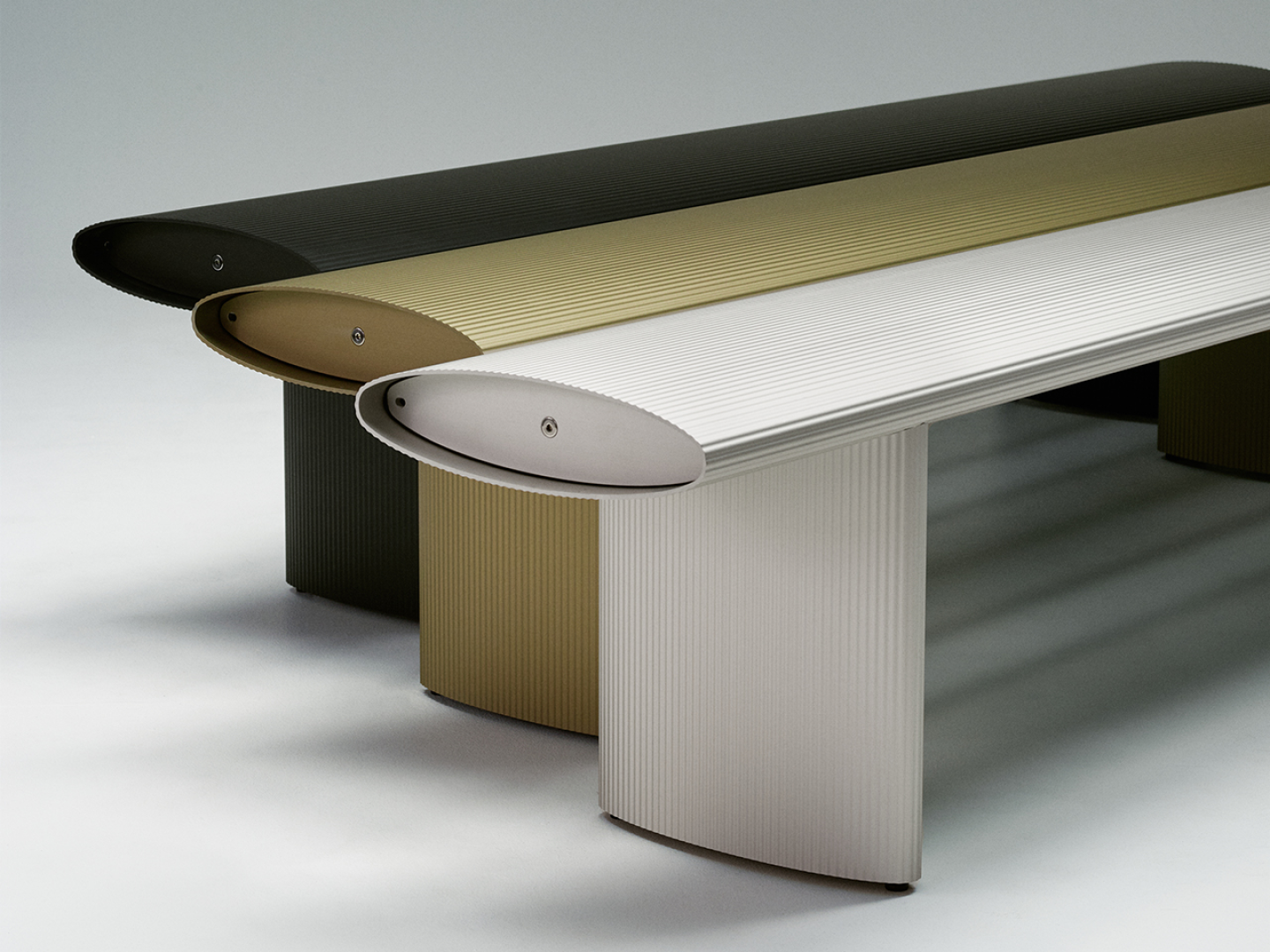
Biotech is booming. As the ingenuities of science and nature open us to new design cultures- how can material innovators flex their influence through evocative, material-led brand storytelling?
Here we unpack 3 critical themes for Material Futures:
Materialising the Brand
Celebrating the Process
Journeys to Market








